In the rapidly evolving landscape of Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) networks, drop cables play a pivotal role in delivering high-speed connectivity directly to end-users. Designed for flexibility, durability, and ease of installation, normal type FTTH drop cables like the GJYXCH, GJYXFCH, GJXFH, GYFXTBY, and GJFJU series are engineered to meet diverse deployment needs in residential, commercial, and industrial environments. This article explores the features, applications, and advantages of these cables, highlighting their importance in modern optical distribution networks.
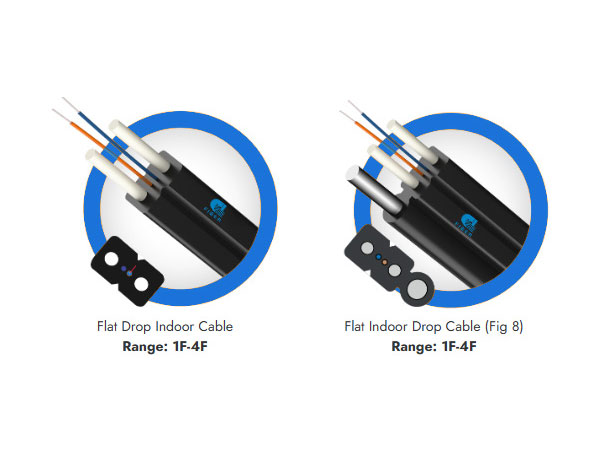

Overview of FTTH Drop Cables
FTTH drop cables are the final link in the fiber optic network, connecting distribution points (e.g., street cabinets or poles) to subscriber premises. These cables prioritize lightweight design, bend resistance, and environmental adaptability to ensure reliable signal transmission in both indoor and outdoor settings. The GJYXCH, GJYXFCH, GJXFH, GYFXTBY, and GJFJU variants cater to specific installation requirements while adhering to industry standards for performance and safety.
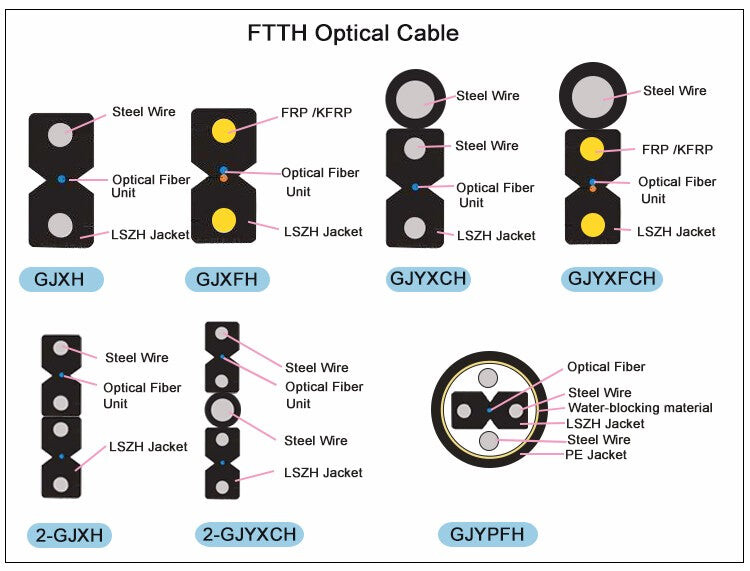
Key Features and Structural Design
Each cable model in this series offers unique structural attributes tailored to different scenarios:
1. GJYXCH Fiber Optic Drop Cable
Structure:
Core: Single-mode or multi-mode optical fibers.
Reinforcement: Central strength member (e.g., FRP or steel wire) for tensile strength.
Jacket: LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) or UV-resistant polyethylene (PE) outer sheath.
Applications: Ideal for aerial or duct installations in outdoor environments.
Key Advantages:
Excellent resistance to moisture and temperature fluctuations.
Lightweight and easy to splice.
2. GJYXFCH Fiber Optic Drop Cable
Structure:
Armor: Incorporates a corrugated steel tape or aluminum layer for enhanced crush resistance.
Sheath: Double-layer design with LSZH outer jacket.
Applications: Suitable for rodent-prone areas or harsh outdoor conditions.
Key Advantages:
Superior mechanical protection without compromising flexibility.
Ideal for direct burial or underground conduits.
3. GJXFH Fiber Optic Drop Cable
Structure:
Design: Flat, ribbon-like shape for space-efficient routing.
Strength Members: Aramid yarn or dielectric rods.
Applications: Perfect for indoor deployments, wall-mounted installations, or tight spaces.
Key Advantages:
Ultra-thin profile with high fiber count density.
Flame-retardant properties comply with indoor safety standards.
Structure:
Armor: Lightweight stainless steel or aluminum interlock armor.
Jacket: Weather-resistant PE with anti-UV additives.
Applications: Aerial installations, especially in regions with extreme weather (e.g., high winds, ice).
Key Advantages:
Self-supporting design eliminates the need for messenger wires.
High tensile strength for long-span deployments.
5. GJFJU Fiber Optic Drop Cable
Structure:
Flexible Design: Tight-buffered fibers with aramid reinforcement.
Outer Sheath: Abrasion-resistant PVC or LSZH.
Applications: Short-distance indoor/outdoor connections, such as wall entries or patch panels.
Key Advantages:
Easy termination and connectorization.
Excellent bend performance (complies with ITU-T G.657 standards).
Common Advantages of the Series
Despite their structural differences, all cables in this series share core benefits:
High Performance: Low attenuation and high bandwidth ensure stable gigabit or 10G connectivity.
Durability: Resistant to moisture, UV radiation, and mechanical stress.
Installation Flexibility: Compatible with aerial, duct, direct burial, and indoor setups.
Safety Compliance: Flame-retardant and low-smoke materials meet IEC/EN and ANSI/TIA standards.
Typical Applications
Residential FTTH Networks: Connecting homes to distribution terminals with minimal visual impact.
Commercial Buildings: Deploying in risers, plenums, or horizontal cabling for offices and campuses.
Industrial Zones: Ruggedized variants (e.g., GJYXFCH) withstand harsh factory environments.
Telecommunication Networks: Rapid deployment for 5G backhaul or last-mile connectivity.

Selection Guidelines
When choosing a cable from this series, consider:
Environment: Outdoor cables (
GYFXTBY, GJYXCH) require UV/weather resistance; indoor cables (GJXFH) prioritize fire safety.
Mechanical Risks: Armored options (
GJYXFCH) protect against rodents or crushing.
Installation Method: Self-supporting (GYFXTBY) vs. lashed or duct-installed cables.
Bend Sensitivity: Opt for bend-insensitive fibers (
GJFJU) in tight routing scenarios.
Conclusion
The
GJYXCH, GJYXFCH, GJXFH, GYFXTBY, and
GJFJU FTTH drop cables exemplify innovation in optical connectivity, balancing robustness, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. Whether bridging the last meter to a suburban home or reinforcing an enterprise network, these cables provide tailored solutions for modern FTTH challenges. By aligning with global standards and adapting to diverse environments, they empower telecom operators and installers to build future-proof, high-performance networks that meet the escalating demands of the digital age.



