The color arrangement for optical fiber cables is standardized to ensure consistent identification of individual fibers during installation, splicing, and maintenance. The TIA/EIA-598-C standard is the most widely followed guideline for color coding in optical fiber cables, both for loose-tube and ribbon fiber cables. Below are the standard color codes and key rules for organizing and identifying optical fibers.
1. TIA/EIA-598-C Standard Color Code for Optical Fibers
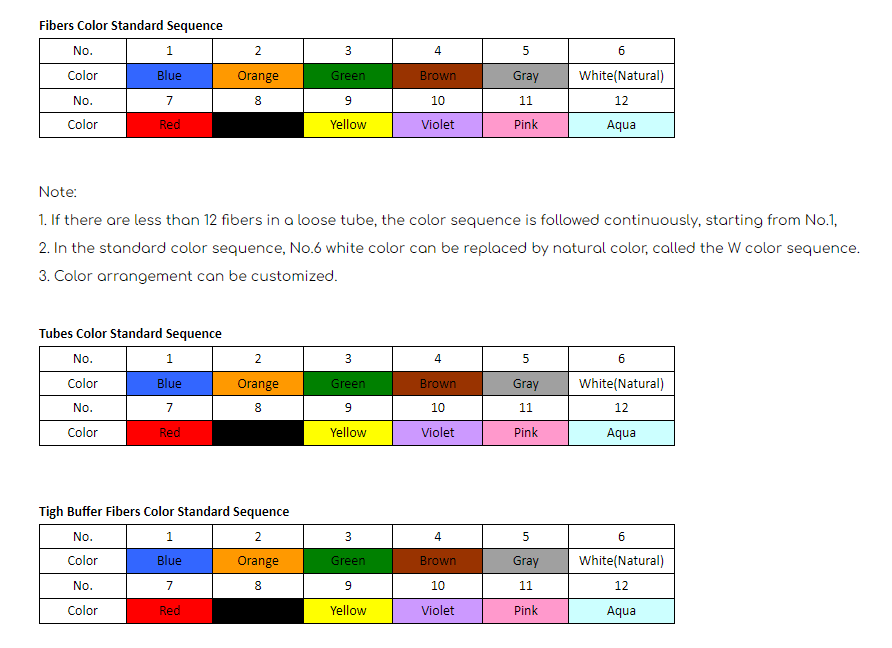
For optical fiber cables, each individual fiber is color-coded in a specific sequence to facilitate easy identification. The standard color sequence is based on a 12-fiber system, which repeats for cables with higher fiber counts.
Color Code for 12 Fibers:
Blue
Orange
Green
Brown
Slate (Gray)
White
Red
Black
Yellow
Violet
Rose (Pink)
Aqua (Light Blue)
For fiber counts higher than 12, the color pattern repeats in groups (bundles) of 12. In these cases, the fibers are typically organized into tubes or groups, and each group is identified by a colored tube.
2. Fiber Color Coding for Loose-Tube Cables
Loose-tube cables are commonly used in outdoor environments and consist of multiple tubes, each containing a set of fibers. The fibers inside each tube follow the standard 12-fiber color code. The tubes themselves are also color-coded for identification.
Tube Color Coding for Loose-Tube Cables (12-Tube Standard):
Blue
Orange
Green
Brown
Slate
White
Red
Black
Yellow
Violet
Rose
Aqua
If the fiber count exceeds the capacity of 12 tubes, a buffer tube stripe or binders (such as rings or dashes) are used to distinguish between the repeated sets.
3. Fiber Color Coding for Ribbon Cables
In ribbon fiber cables, multiple fibers are arranged side-by-side in a flat, ribbon-like formation. The color code for each individual fiber in a ribbon also follows the same 12-color sequence as outlined by the TIA/EIA-598-C standard.
Example for a 12-Fiber Ribbon:
Ribbon 1: Blue, Orange, Green, Brown, Slate, White, Red, Black, Yellow, Violet, Rose, Aqua
Ribbon 2 and higher: The same color sequence is repeated for each ribbon layer, allowing for easier identification of fibers within high-fiber-count cables.
4. Color Coding for Tight-Buffered Cables (Indoor Use)
Indoor fiber optic cables, especially those with a lower fiber count (typically 6, 12, 24, etc.), often use tight-buffered fibers. These fibers are color-coded individually following the standard TIA/EIA-598-C sequence.
For indoor cables with fewer than 12 fibers, the same standard color code is applied to identify each fiber. For cables with more than 12 fibers, the color sequence repeats.
5. Jacket Color Coding for Fiber Types
In addition to the color coding of individual fibers, the outer jacket of the cable itself is often color-coded to indicate the type of fiber being used. This allows installers and technicians to identify the type of fiber (single-mode or multimode) without cutting the cable open.
Jacket Color Code:
Yellow: Single-mode fiber (OS1, OS2)
Orange: Multimode fiber (OM1, OM2)
Aqua: Laser-optimized multimode fiber (OM3, OM4, OM5)
Erika Violet: Some OM4 multimode fibers
6. Additional Markers
In some cases, additional markers such as ring markings, stripes, or tracers are used to differentiate between bundles, ribbons, or individual fibers when higher fiber counts are involved.
Ring Markings: Small colored rings on the fiber coating indicate different fiber groups when the color sequence repeats.
Stripes: For high-fiber-count cables, stripes on the jacket or buffer tubes are sometimes used to differentiate between groups of fibers.
7. Buffer Tube and Fiber Bundling
For cables with more than 12 fibers, fibers are often divided into groups (bundles) and placed in buffer tubes. The buffer tubes are color-coded according to the standard sequence, and the fibers inside the tubes follow the standard 12-fiber color code. For large fiber counts, tubes or fibers may also have additional markings, such as stripes or rings, to avoid confusion.
Conclusion
The color arrangement rules for optical fibers, as outlined by the TIA/EIA-598-C standard, provide a consistent method for identifying fibers in both indoor and outdoor fiber optic cables. Whether the cable contains 6, 12, 24, or more fibers, this color-coding system ensures that each fiber can be easily located and distinguished during installation, splicing, or repairs.

